

< Previous | Contents | Next >
Section 5 Crankshafts under special requirements
501. Application
The requirements in this Section apply to the tests and inspection for the approval of crankshafts manufactured to reduce the dimension in accordance with the requirements of Pt 5, Ch 2, 208, Pt 2, Ch 1, 501. 13 and 601. 14 of the Rules in case where the special manufacturing processes specified in the following (1) or (2) are adopted.
(1) The special forging process, namely continuous grain forging method (e.g. RR forging, TR forg- ing or stamp forging), other than the free forging methods (block forging, upset & twisting
forging and upsetting forging) used for manufacture of solid crankshaft and block forging meth-
od used for manufacture of semi-builtup crankshafts.
(2) The manufacturing processes using the surface treatments such as induction hardening, cold-roll- ing and nitriding. However, semi-builtup crank throw manufactured under special manufacturing process in the preceding (1) is excluded.
502. Data to be submitted
The manufacturer who intends to obtain an approval for the manufacturing process is to submit an application together with the data specified in 102., containing information of applicable engine type, or with the data showing the details of surface treatment in the case of 501. (2).
503. Approval tests
1. Kinds of steel
The tests are to be carried out for each kind of steels as a standard practice. Even within the cat- egory of steel forgings, normalized steels (including annealed steels or annealed steels after normal- ization) and quenched and tempered steels are to be considered as different kind of steels. However, for example, in case where it is intended to obtain approval for carbon steel forgings in both RSF 520 and RSF 560, tests on RSF 560 which has a higher tensile strength are to be carried out as the standard procedure. The same principle is to apply in dealing with Cr-Mo steel forgings and Ni-Cr-Mo steel forgings.
2. Approval test for special forged crankshafts
(1) Test specimens
The test specimen, as standard, is to be taken from the crankthrow with the maximum diameter manufactured or close thereto.
(2) Tests
The following tests are to be carried out on each test specimen:
(A) Sulphur print test and macro-structure analysis (The specimens are to be taken from sections
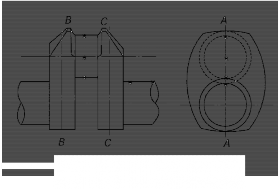
A-A, B-B and C-C specified in Fig 2.5.1)
Fig 2.5.1 Sampling Positions
(B) Chemical composition analysis test (The specimens are to be taken from the positions aster- isked in Fig 2.5.1)
(C) Micro-structure analysis (The specimens are to be taken from the positions asterisked in Fig 2.5.1)
Guidance for Approval of Manufacturing Process and Type Approval, Etc. 2015 25
Ch 2 Approval of Manufacturing Process Ch 2, Sec 5
![]()
(D) Microscopic test for the non-metallic inclusions (as per KS D 0204) (The specimens are to be taken from the positions asterisked in Fig 2.5.1)
(E) Hardness test (Positions in the vicinity of pin or journal surface. In the case of quenched
and tempered steels, hardness distribution from the surface to the shaft centre.)
(F) Tensile test standard.)
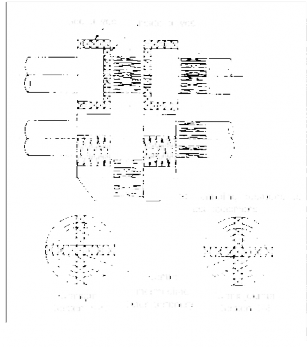
and impact test (Test specimens are to be taken as specified in Fig 2.5.2 as the
Fig 2.5.2 Sampling Positions of Test Specimens
(G) Bending fatigue test on actual crank throw. The number of test specimens more
is to be two or
(H) Rotational bending fatigue test on small-size test specimens (Dia. 10 ~ 20 mm ). The number

of test specimens is to be not less than 10 as the standard. In case where previous data on this test are available or in case of carbon steel forgings, this test may be omitted upon ap- proval of the Society. (Fig 2.5.3)
Fig 2.5.3 Sampling Positions of Bend Test Specimens
(3) Judgement of test results
The manufacturing process can be approved in case where the results of tests of the preceding
(2) proves that the special forged crankshaft has continuous grain flow, the product quality is
judged stable and the fatigue strength obtained from (2) (g) have improved by 20 % or more
when compared with the fatigue strength of a free-forged crankshaft ( ) calculated by the following formula:
26 Guidance for Approval of Manufacturing Process and Type Approval, Etc. 2015
Ch 2 Approval of Manufacturing Process Ch 2, Sec 5
![]()
When
When 100< <200,
When
where
: Diameter of test specimen (mm)
: Specified minimum tensile strength (N mm
3. Approval tests for crankshafts with surface treatments
This requirement applies to cases where the fillets of a crankshaft are applied with induction hard- ening, cold-rolling or nitriding, etc. In case where surface treatment is applied to all over the crankpin, journal and fillets, approval tests are to be as deemed appropriate by the Society.
(1) Test specimens
The requirements specified in 2 (1) apply correspondingly.
(2) Tests
The following tests are to be carried out on each test specimen:
(A) Non-destructive test (the conditions of defects on surface of the test specimens before and after the surface treatment are to be examined. The detection is to be either by magnetic particle test or liquid penetrant test.)
(B) Examination of the hardness distribution, depth of hardening and residual stress (Examination is to be carried out on the surface treated areas and their vicinity. Further, in case where cold-rolling is carried out, measurements for the deformation on the cold-rolling area are to be included.)
(C) Sulphur print test, microstructure test and macroscopic test (to be carried out on the sec- tional area in the direction of hardening depth.)
(D) Bending fatigue test on actual crank throw (tests are, in principle, to be carried out on both
the crank throws with and without surface treatment. In this case, the number of test speci- mens are to be sufficient to verify the strength improvement ratio specified in Pt 5, Ch
2,
208. 1 of the Guidance relating to the Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships. In this connection, the torsional fatigue tests on the actual crank throws or the test specimens hav- ing sizes similar to them are also to be carried out.)
(E) Tensile test and impact test (one set of test specimens as to be taken from end portion of crankshaft with surface treatment.)
(3) Judgement of test results
The manufacturing process can be approved in case when the results of tests of preceding item
(2) prove that a stability in the quality of the crankshafts with surface treatment and excellent improvement in the fatigue strength are obtained. In this case, the allowable stress is to be as specified in Pt 5, Ch 2, 208. 1 of the Guidance relating to the Rules for the Classification of
4. Steel Ships.
501. (1) is applied with the surface treatment as specified in, 501. (2), the judgement for accept-
ance is to be determined by considering the results of tests for free forged crankshaft with
treatment and the strength of other positions of the crankshaft than the fillets thereof.
surface
Guidance for Approval of Manufacturing Process and Type Approval, Etc. 2015 27
Ch 2 Approval of Manufacturing Process Ch 2, Sec 6
![]()